Materials
Free-cutting steel
Free-cutting steels are designed for high-speed mechanical machining, i.e. by removing material.
Rich in sulphur, this allows them to promote the crumbling of chips. They also have the advantage of reducing friction between tools and parts.
There are different types depending on the expected needs:
- standard steels
- hardening steels
- tempering steels
- steels for carburizing
- ...
Free-cutting steels are delivered in the form of bars, tubes... They are then machined, which requires high precision and high production. and finally, they undergo, depending on the need, a heat treatment.


Case-hardening steel
Case-hardened steels are defined by a carbon content of less than 0.25%
Carburizing improves resistance, it is intended to harden the surface of a part.
Nitriding steel
Nitriding steel is obtained following a surface treatment which consists of incorporating nitrogen into the surface layer of a steel, in order to modify its mechanical properties.
Nitriding improves wear resistance, surface hardness and toughness.

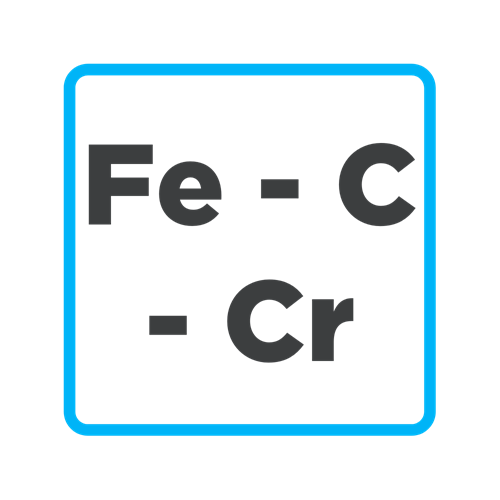
Stainless steel
Stainless steel, also called stainless steel, is a ferrous metal alloy.
It contains more than 50% iron, a minimum of 10.5% chromium and a maximum of 1.2% carbon.
It is recognized for its various characteristics:
- high corrosion resistance
- oxidation resistance
- economic
- total recyclability
- good mechanical strength/weight ratio
There are several types of stainless steels: austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, duplex
Aluminum
Aluminum is the first of the non-ferrous metals.
It contains bauxite, a mixture of alumina (40-60%), silicon oxide (2-12%), iron oxide (18-25%), titanium oxide (2-4 %) and water (10 to 15%).
It is recognized for its various characteristics:
- inalterability
- low density
- resistance and especially to corrosion
- good conductor of electricity and heat
- recyclable
It is able to accept a wide variety of surface treatments.


Titanium
Titanium is a transition metal.
It can be alloyed with iron and aluminum among other elements.
It is recognized for its various characteristics:
- lightness
- high corrosion resistance
- resistance to erosion and fire
- bio compatibility
- ductility
Titanium makes it possible to manufacture thin and light parts.
Bronze
Bronze is a non-ferrous metal alloy.
Historically made of copper, tin, zinc and lead, it is now primarily an alloy of copper and tin.
It is recognized for its various characteristics:
- high wear resistance
- corrosion resistance
- good electrical conductivity
It is very often used as a friction material in front of steel.


Brass
Bronze is a non-ferrous metal alloy.
It is made up of copper and zinc.
It is recognized for its various characteristics:
- high mechanical resistance
- increase in lifespan
- reduction of the melting point of the metal
- good electrical conductivity
- easy to machine
- good corrosion resistance
A question about the materials DPM works with?
Need information on the different types of metals?

